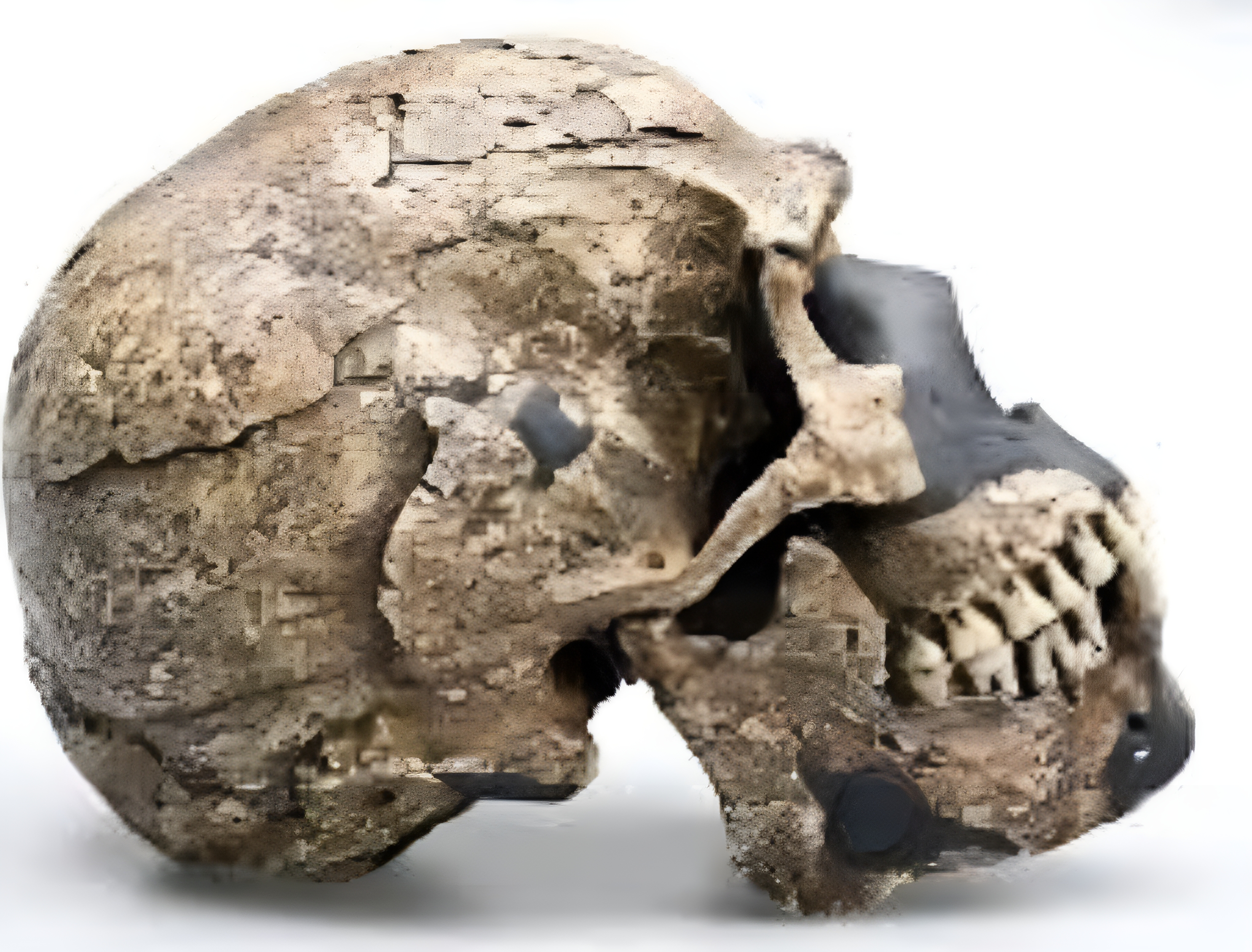
A Groundbreaking Discovery in Human Ancestry
A newly uncovered fossil, believed to be the oldest Homo sapiens remains ever found, is challenging long-standing theories about the origins and migration of our species. The discovery, made in a previously unexplored archaeological site, suggests that Homo sapiens may have emerged far earlier than previously thought, potentially rewriting the timeline of human evolution.
Unveiling the Oldest Homo Sapiens Fossil
Archaeologists and paleoanthropologists uncovered the fossilized remains in a region that was not traditionally considered central to early human evolution. Initial dating techniques indicate that the fossil is significantly older than previous specimens, pushing back the estimated emergence of modern humans by thousands of years. If confirmed, this finding would require scientists to reassess the evolutionary journey of Homo sapiens and how they dispersed across the globe.
Challenging Existing Theories on Human Evolution
For decades, prevailing theories have suggested that Homo sapiens evolved in a single region before migrating outward. However, this new fossil raises the possibility of multiple evolutionary hotspots where early human populations developed simultaneously. This challenges the widely accepted “Out of Africa” theory and may support the idea of a more complex, intertwined evolutionary path.
Implications for Human Migration and Adaptation
The discovery not only extends the timeline of human existence but also provides crucial insights into how our ancestors adapted to different environments. The location of the fossil suggests that early Homo sapiens may have been more widespread than previously assumed, adapting to diverse landscapes and climates much earlier in history. This could explain the variations seen in early human populations across different regions.
Future Research and Scientific Debate
While this finding is groundbreaking, further research is necessary to validate the fossil’s age and significance. Scientists are now conducting detailed DNA analysis, geological studies, and comparative research to determine its exact place in the evolutionary timeline. The discovery is expected to ignite new debates within the scientific community, potentially leading to a revised understanding of human origins and migration patterns.
The unveiling of the oldest known Homo sapiens fossil is a historic moment in the field of anthropology, shedding new light on the complexities of human evolution. As researchers continue to study this remarkable find, we may soon gain a deeper understanding of our species’ true origins and the diverse paths our ancestors took to shape the modern human world.